TCP or IP
TCP/IP model
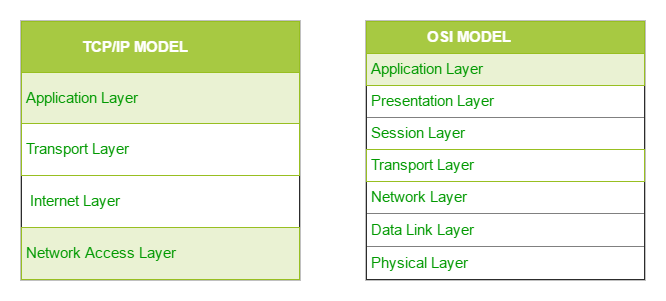
- The TCP/IP model was developed prior to the OSI model.
- The TCP/IP model is not exactly similar to the OSI model.
- The TCP/IP model consists of five layers: the application layer, transport layer, network layer or internet layer , data link layer and physical layer(Network Access Layer).
- The first four layers provide physical standards, network interface, internetworking, and transport functions that correspond to the first four layers of the OSI model and these four layers are represented in TCP/IP model by a single layer called the application layer.
- TCP/IP is a hierarchical protocol made up of interactive modules, and each of them provides specific functionality.
Functions of TCP/IP layers:
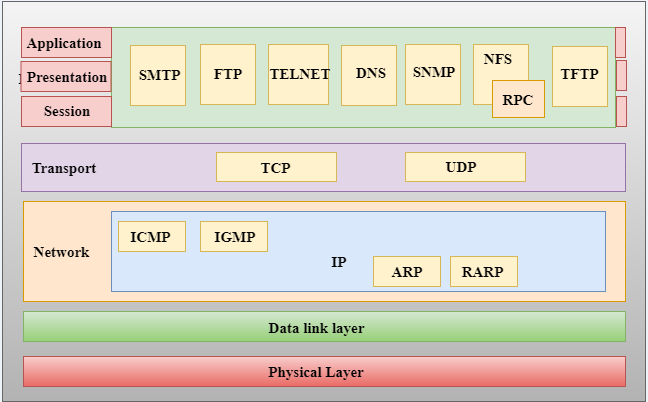
Network Access Layer
- A network layer is the lowest layer of the TCP/IP model.
- A network layer is the combination of the Physical layer and Data Link layer defined in the OSI reference model.
- It defines how the data should be sent physically through the network.
- This layer is mainly responsible for the transmission of the data between two devices on the same network.
- The functions carried out by this layer are encapsulating the IP datagram into frames transmitted by the network and mapping of IP addresses into physical addresses.
- The protocols used by this layer are ethernet, token ring, FDDI, X.25, frame relay.
Internet layer
- An internet layer is the second layer of the TCP/IP model.
- An internet layer is also known as the network layer.
- The main responsibility of the internet layer is to send the packets from any network, and they arrive at the destination irrespective of the route they take.
Following are the protocols used in this layer are:
IP Protocol: IP protocol is used in this layer, and it is the most significant part of the entire TCP/IP suite.
Following are the responsibilities of this protocol:
- IP Addressing: This protocol implements logical host addresses known as IP addresses. The IP addresses are used by the internet and higher layers to identify the device and to provide internetwork routing.
- Host-to-host communication: It determines the path through which the data is to be transmitted.
- Data Encapsulation and Formatting: An IP protocol accepts the data from the transport layer protocol. An IP protocol ensures that the data is sent and received securely, it encapsulates the data into message known as IP datagram.
- Fragmentation and Reassembly: The limit imposed on the size of the IP datagram by data link layer protocol is known as Maximum Transmission unit (MTU). If the size of IP datagram is greater than the MTU unit, then the IP protocol splits the datagram into smaller units so that they can travel over the local network. Fragmentation can be done by the sender or intermediate router. At the receiver side, all the fragments are reassembled to form an original message.
- Routing: When IP datagram is sent over the same local network such as LAN, MAN, WAN, it is known as direct delivery. When source and destination are on the distant network, then the IP datagram is sent indirectly. This can be accomplished by routing the IP datagram through various devices such as routers.
- ARP stands for Address Resolution Protocol.
- ARP is a network layer protocol which is used to find the physical address from the IP address.
- The two terms are mainly associated with the ARP Protocol:
- ARP request: When a sender wants to know the physical address of the device, it broadcasts the ARP request to the network.
- ARP reply: Every device attached to the network will accept the ARP request and process the request, but only recipient recognize the IP address and sends back its physical address in the form of ARP reply. The recipient adds the physical address both to its cache memory and to the datagram header
- ICMP stands for Internet Control Message Protocol.
- It is a mechanism used by the hosts or routers to send notifications regarding datagram problems back to the sender.
- A datagram travels from router-to-router until it reaches its destination. If a router is unable to route the data because of some unusual conditions such as disabled links, a device is on fire or network congestion, then the ICMP protocol is used to inform the sender that the datagram is undeliverable.
- An ICMP protocol mainly uses two terms:
- ICMP Test: ICMP Test is used to test whether the destination is reachable or not.
- ICMP Reply: ICMP Reply is used to check whether the destination device is responding or not.
- The core responsibility of the ICMP protocol is to report the problems, not correct them. The responsibility of the correction lies with the sender.
- ICMP can send the messages only to the source, but not to the intermediate routers because the IP datagram carries the addresses of the source and destination but not of the router that it is passed to.
The two protocols used in the transport layer are User Datagram protocol and Transmission control protocol.
- User Datagram Protocol (UDP)
- It provides connectionless service and end-to-end delivery of transmission.
- It is an unreliable protocol as it discovers the errors but not specify the error.
- User Datagram Protocol discovers the error, and ICMP protocol reports the error to the sender that user datagram has been damaged.
- UDP consists of the following fields:
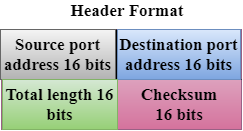
Source port address: The source port address is the address of the application program that has created the message.
Destination port address: The destination port address is the address of the application program that receives the message.
Total length: It defines the total number of bytes of the user datagram in bytes.
Checksum: The checksum is a 16-bit field used in error detection. - UDP does not specify which packet is lost. UDP contains only checksum; it does not contain any ID of a data segment.
- Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)
- It provides a full transport layer services to applications.
- It creates a virtual circuit between the sender and receiver, and it is active for the duration of the transmission.
- TCP is a reliable protocol as it detects the error and retransmits the damaged frames. Therefore, it ensures all the segments must be received and acknowledged before the transmission is considered to be completed and a virtual circuit is discarded.
- At the sending end, TCP divides the whole message into smaller units known as segment, and each segment contains a sequence number which is required for reordering the frames to form an original message.
- At the receiving end, TCP collects all the segments and reorders them based on sequence numbers.
Application Layer
- An application layer is the topmost layer in the TCP/IP model.
- It is responsible for handling high-level protocols, issues of representation.
- This layer allows the user to interact with the application.
- When one application layer protocol wants to communicate with another application layer, it forwards its data to the transport layer.
- There is an ambiguity occurs in the application layer. Every application cannot be placed inside the application layer except those who interact with the communication system. For example: text editor cannot be considered in application layer while web browser using HTTP protocol to interact with the network where HTTP protocol is an application layer protocol.
Following are the main protocols used in the application layer:
- HTTP: HTTP stands for Hypertext transfer protocol. This protocol allows us to access the data over the world wide web. It transfers the data in the form of plain text, audio, video. It is known as a Hypertext transfer protocol as it has the efficiency to use in a hypertext environment where there are rapid jumps from one document to another.
- SNMP: SNMP stands for Simple Network Management Protocol. It is a framework used for managing the devices on the internet by using the TCP/IP protocol suite.
- SMTP: SMTP stands for Simple mail transfer protocol. The TCP/IP protocol that supports the e-mail is known as a Simple mail transfer protocol. This protocol is used to send the data to another e-mail address.
- DNS: DNS stands for Domain Name System. An IP address is used to identify the connection of a host to the internet uniquely. But, people prefer to use the names instead of addresses. Therefore, the system that maps the name to the address is known as Domain Name System.
- TELNET: It is an abbreviation for Terminal Network. It establishes the connection between the local computer and remote computer in such a way that the local terminal appears to be a terminal at the remote system.
- FTP: FTP stands for File Transfer Protocol. FTP is a standard internet protocol used for transmitting the files from one computer to another computer.